DynamoDB vs MongoDb
2017-10-03The essential difference between these two NoSql databases is not only the syntax and the query principle, but also an important point of the architecture itself and the accompanying services.
Amazon Cloud Platform assumes responsibility for installation, maintenance and implementation of all additional services. All that you need is to click on the required elements in a management console. Definitely, payment is charged for separate moments. At the same time, not the fact of adjustment, but the intensity of use is the basic idea of payment in Amazon DynamoDb. It is good for applications which can significantly expand in the future. When choosing DynamoDb, it will occur without significant efforts from the developers. So, you can increase the bandwidth, make replicas of the database in different regions, adjust the data consistency, provide security policy and so on in few clicks.
There is a local version of DynamoDb. Its application is basically taken down to the development and testing of the application and the database. However, DynamoDb is usually used as an Amazon service. While MongoDb is often installed and configured locally on the server.
Query Features in DynamoDB and MongoDb
If you pay attention to the query language working with DynamoDb, you may notice some crockness, in comparison with MongoDb, when trying to use complex structures. It should be noted that there are various restrictions when working with queries in DynamoDb, the main idea is to work through keys. In this database, you can observe a clear and fixed separation of key (sorted and partition keys) and non-vehicle fields. There exists such functionality as indexes: local and global for different types of work with data, not only by the key.
But working with it requires additional practice. Also, certain restrictions are placed on indexes that affect the following points: the number of indexes per table (you can enter no more than 5 of each type), the format of the queries (in particular the partition key), which in turn complicates the search by non-vehicle fields.
It should be taken into account that local indexes are created at the time of creating the table, so it is worthwhile to consider the necessity of having them in beforehand.
MongoDb also contains indexes, but with a larger variety of syntax.
Organization of Pagination in DynamoDB and MongoDb
You can observe a significant difference in such parameter as limit, which can be summarized as follows: in DynamoDb this is the limit on the number of records to be viewed, in MongoDb - the restriction of the records found or returned. Thus, in DynamoDB you can't find just the first 5 values of the corresponding filters, sooner check the 5 elements, and there will be a probability of not getting actual results if no match for the condition.
This ideological difference in the performance of these properties affects the organization of such moments as pagination and sorting (on the side of the database) of the supplied data from the tables. So MongoDb has built-in functions that allow to implement the above-mentioned functionality - skip(Number) (allows to skip the required amount), limit(Number) and sort(). You have to make more efforts to implement both pagination and data sorting in DynamoDb. One of the ideas for sorting the data supplied with DynamoDb is to create an additional 'create time' field for the record and assign its partition to the global index, and use the original partition table key as the sort key.
Other Significant Differences between DynamoDB and MongoDb
Among advantages of DynamoDb are:
- Automation of performance monitoring and minimization of delays in updating data, even in different regions.
- Amazon allows you to configure alerts for various critical changes.
BUT a strong disadvantage here is the following:
- You need to change the configuration, create additional replicas, clusters, implement sharding in MongoDb in manual mode, which is very problematic for an already running application.
As for transactions on the principle of sql, as well as in many NoSql databases, they are not provided. However, in MongoDb this mechanism can be implemented using atomic operations, for example findAndModify(document), etc.
Fields in DynamoDb are limited to 400kb, while in MongoDb this property can be customized in any order.
MongoDb allows you to implement the services that you will find in DynamoDb, but it will require more efforts from the developers, although it will provide awareness of the actions.
In addition, MongoDb libraries have been written for more languages.
Performance Graphs
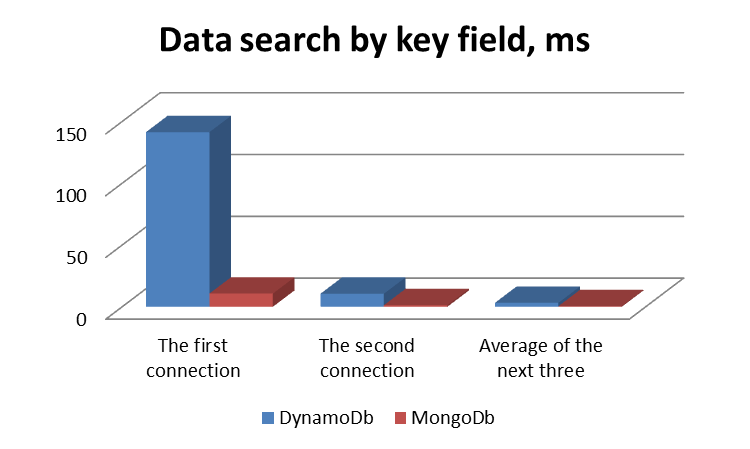
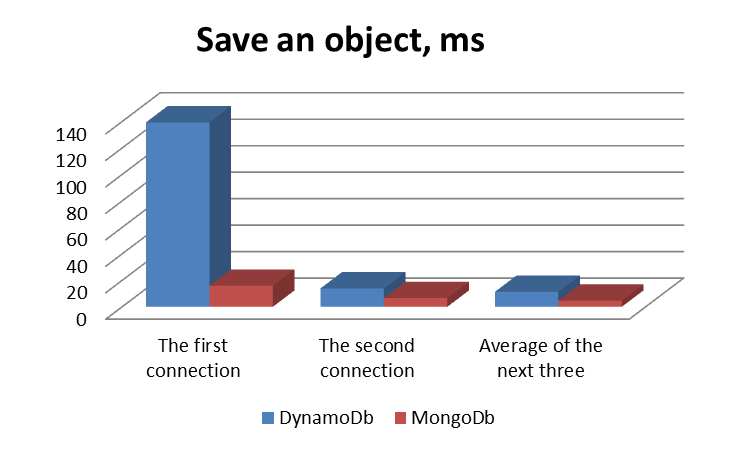
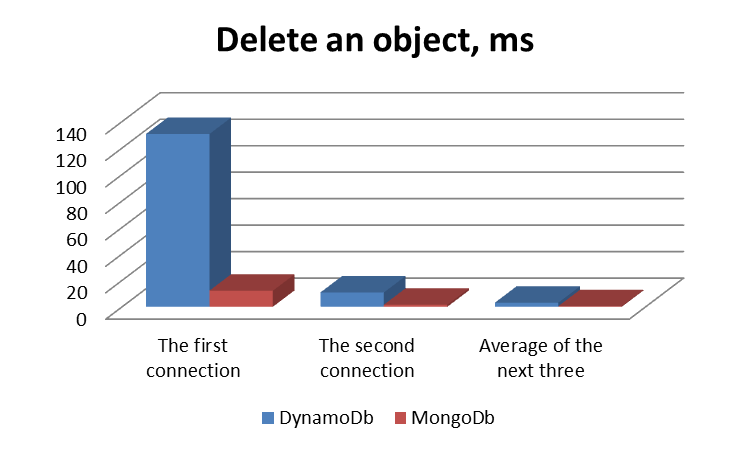
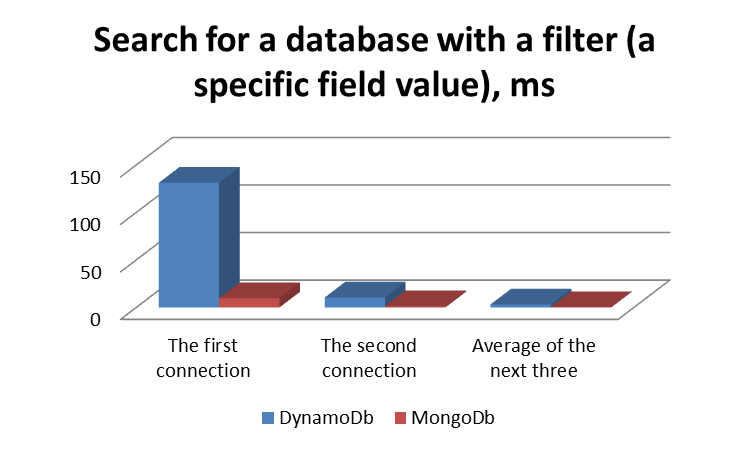
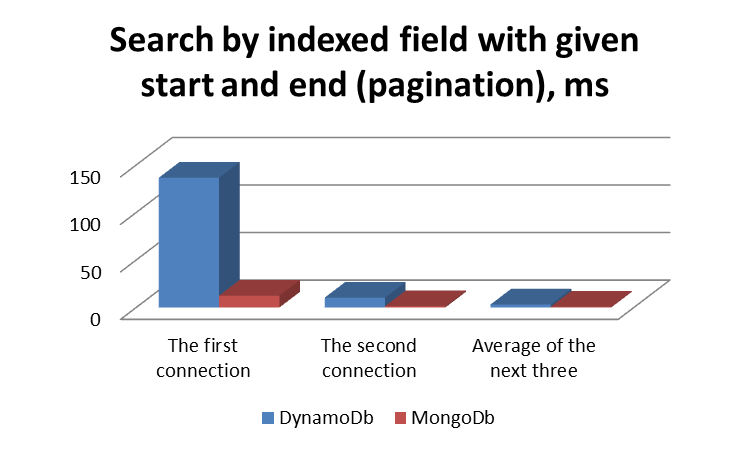
Conclusion
In conclusion I want to summarize that DynamoDB and MongoDb are widespread representatives of NoSql databases, with many advantages, but also with certain shortcomings, in particular difference in performance. So, ease of maintenance is accompanied by some limitations, and vice versa, the configuration of everything needed is maximally controlled, which also affects the complexity of the process. Therefore, you have to carefully study which manipulations with the base are required by your application and choose the most suitable reasoning from this.
